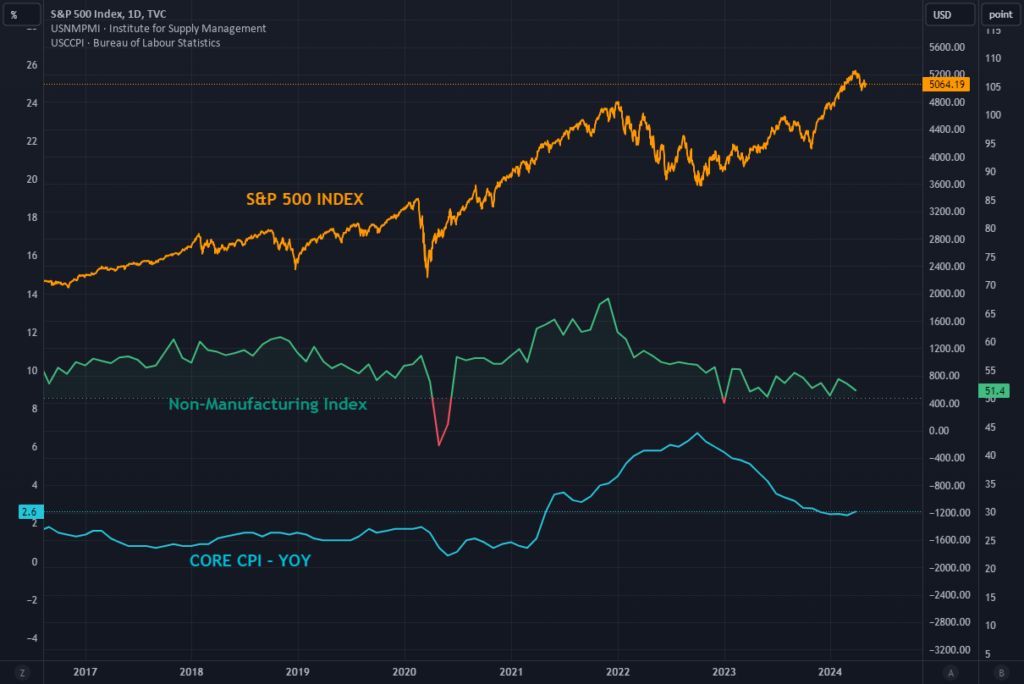
The world of finance is a complex web of interconnected factors, and seemingly disparate indices can influence each other in unexpected ways. this house, S&P500, Core CPI (Personal consumption expenditure price index), and the Non-manufacturing index It stands out as an important indicator of economic health. Understanding those relationships is important for investors, economists, and policy makers alike.
of S&P500The stock index, also known simply as “S&P,” is a stock index that measures the performance of the 500 largest companies listed on U.S. stock exchanges. It is widely recognized as one of the The best indicator of overall health in the United States. the stock market and, by extension, the broader economy. When the S&P 500 rises, it generally indicates investor confidence and economic growth.
on the other hand, Core CPI It tracks changes in the prices of goods and services consumed by households, with the exception of food and energy prices, which are more volatile. As a measure of inflation, Core PCI provides insight into consumer purchasing power and overall cost of living. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, closely monitor inflation trends to inform monetary policy decisions.
Non-manufacturing index, also known as ISM Non-Manufacturing Indexmeasures economic activity in the services sector, which includes industries such as retail, healthcare, finance, and transportation.reading over 50 indicates the expansion and the reading is less than 50 It suggests contraction. The modern economy is dominated by services, making the non-manufacturing index an important barometer of economic health and consumer sentiment.
So how do these indices relate to each other?
First, the S&P 500 and non-manufacturing indexes often move in tandem. Because the services sector is an important part of the U.S. economy, positive data from non-manufacturing indexes tends to increase investor confidence, leading to higher stock prices as reflected in the S&P 500. Conversely, a decline in the non-manufacturing index is likely. It signals a weak economy and could cause the S&P 500 to decline.
Second, the core CPI plays an important role in monetary policy decisions. Central banks use inflation data to adjust interest rates and introduce other monetary tools to stabilize the economy. A rise in core CPI could cause the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates and tighten monetary policy to curb inflation, potentially reducing stock market returns represented by the S&P 500.
In summary, the relationship between the S&P 500, core CPI, and nonmanufacturing index highlights their interdependence. financial market, consumer behaviorand economic activity. Investors and policymakers should work together to carefully analyze these indices to gain a comprehensive understanding of the current economic situation and make informed decisions.